
|
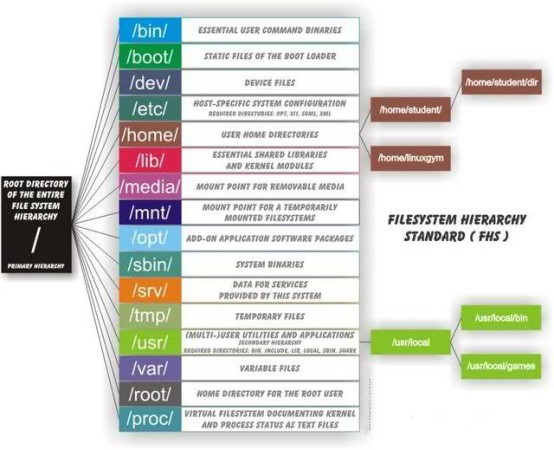
Directory
|
Description
|
|
/bin
|
All binaries needed for the boot process and to run
the system in single-user mode, including essential commands such as cd, ls,
etc.
|
|
/boot
|
Holds files used during the boot process along with
the Linux kernel itself
|
|
/dev
|
Contains device files for all hardware devices on the
system
|
|
/etc
|
Files used by application subsystems such as mail, the
Oracle database, etc.
|
|
/etc/init.d
|
Contains various service startup
scripts
|
|
/etc/profile.d
|
Holds application setup scripts run by /etc/profile
upon login
|
|
/etc/rc.d
|
Contains subdirectories which contain run level
specific scripts
|
|
/etc/rc.d/init.d
|
run level initialization
scripts
|
|
/etc/rc.d/rc?.d
|
Where ‘?’ is a number corresponding to the default run
level. Contains symbolic links to scripts which are in /etc/rc.d/init.d. For
services to be started and stopped at the indicated run
level.
|
|
/etc/skel
|
Holds example dot files used to populate a new user’s
home directory.
|
|
/etc/X11
|
Contains subdirectories and configuration files for
the X Window system
|
|
/home
|
User home directories
|
|
/lib
|
Some shared library directories, files, and
links
|
|
/mnt
|
The typical mount point for the user-mountable devices
such as floppy drives and CDROM
|
|
/proc
|
Virtual file system that provides system
statistics. It doesn’t contain real files but provides an interface to
runtime system information.
|
|
/root
|
Home directory for the root
user
|
|
/sbin
|
Commands used by the super user for system
administrative functions
|
|
/tmp
|
A standard repository for temporary files created by
applications and users.
|
|
/usr
|
Directory contains subdirectories with source code,
programs, libraries, documentation, etc.
|
|
/usr/bin
|
Contains commands available to normal
users
|
|
/usr/bin/X11
|
X Window system binaries
|
|
/usr/include
|
Holds include files used in C
programs
|
|
/usr/share
|
Contains shared directories for man files, info files,
etc.
|
|
/usr/lib
|
Library files searched by the linker when programs are
compiled
|
|
/usr/local/bin
|
Common executable application files local to this
system
|
|
/usr/sbin
|
Commands used by the super user for system
administrative functions
|
|
/var
|
Administrative files such as log files, locks, spool
files, and temporary files used by various
utilities
|
|
/var/www/vhosts/domain1
|
Contains on my v-server the user directory for a
specific domain which is hosted on this serve
|
|
/etc/issue
|
Contains the Ubuntu version you are
running. Contains the pre-login message, often overwritten by
the /etc/rc.d/rc.local script in Red Hat and some other rpm-based Linux
distributions
|
|
lsb_release -a
|
Prints out the Ubuntu version you are
running
|
|
/etc/apt/source.list
|
Contains the available sources for software
installation
|
|
/usr/share/tomcat
|
Installation directory for
tomcat
|
|
echo
$VARIABLE
|
Prints the content of the
environment variable
|
|
sudo /etc/init.d/tomcat5
start/stop
|
Start / stops the tomcat
server
|
|
sudo
-i
|
Switches to
root
|
|
/etc/rsyslog.conf
|
Log messages related to system
|
|
etc/shadow
|
Stores Password in encrypted
form
|
|
/etc/rc.d/rc
|
Defines which services to
start
|
|
/var/log/dmesg
|
Boot time hardware detection and
driver setup. Kernel messages taken just after control. kernel boot messages
|
|
/var/log/maillog
|
Mail System Messages
|
|
/var/log/secure
|
Security ,authentication &
Xinetd messages
|
|
/var/log/audit.audit.log
|
Kernel auditing
messages
|
|
/var/log/lastlog
|
Stores information about the last boot
process
|
|
/var/log/messages
|
Contains messages produced by the syslog daemon during
the boot process.General system messages, includes most of what is
in dmesg if it hasn’t
“rolled over”.
Std. system error messages
|
|
/var/log/wtmp
|
A binary data file holding login time and duration for
each user currently on the system
|
|
/boot/vmlinuz
|
The Linux kernel file. File naming conventions
may include release information. The typical location and name of the Linux
kernel
|
|
/dev/fd0
|
Device file for the first floppy disk drive on the
system
|
|
/dev/fd0H1440
|
Device driver for the first floppy drive in high
density mode, commonly invoked when formatting a floppy diskette for that
density
|
|
/dev/hda
|
Device file for the first IDE hard drive on the
system
|
|
/dev/hdc
|
Commonly, the IDE CDROM drive device file which often
is a symbolic link called to /dev/cdrom, the real CDROM driver
file.
|
|
/dev/null
|
A dummy device which contains nothing. It is
sometimes useful to send output to this device to make it go away forever. used
when you want to send output into oblivion
|
|
/etc/crontab
|
A parent shell script to run commands
periodically. It invokes hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly
scripts.
|
|
/etc/anacrontab
|
Runs the job that did not run when the comp. is
down
|
|
/etc/exports
|
Contains a list of filesystems which may be made
available to other systems on the network via NFS. Specifies hosts to which
file systems can be exported using NFS. Man exports contain information on how
to set up this file for remote users.
|
|
/etc/fstab
|
The file system table contains the description of what
disk devices are available at what mount points. contains information on
partitions and file systems used by system to mount different partitions and
devices on the directory tree
|
|
/etc/mtab
|
Display the currently mounted
system
|
|
/etc/group
|
Holds information regarding security group
definitions.
|
|
/etc/grub.conf
|
The grub boot loader configuration
file
|
|
/etc/hosts
|
Contains host names and their corresponding IP
addresses used for name resolution whenever a DNS server is
unavailable
|
|
/etc/hosts.allow
|
Contains a list of hosts allowed to access services on
this computer.
|
|
/etc/hosts.deny
|
Contains a list of hosts forbidden to access services
on this computer.
|
|
/etc/lilo.conf
|
The lilo boot loader configuration
file
|
|
/etc/modules.conf
|
Holds options for configurable system
modules
|
|
/etc/bashrc
|
system-wide default functions and aliases for the bash
shell
|
|
/etc/conf.modules
|
aliases and options for configurable
modules
|
|
/etc/DIR_COLORS
|
Used to store colors for different file types when
using ls command. The dircolors command uses this file when there is not a .dir
colors file in the user’s home directory. Used in conjunction with the eval
command (see below).
|
|
/etc/HOSTNAME
|
Stores the name of the host computer(Used in
Debian).For Red Hat Linux it would be
/etc/sysconfig/network.
|
|
/etc/passwd .
|
Contains passwords and other information concerning
users who are registered to use the system. For obvious security reasons, this
is writable only by root and readble by others. It can be modified by root
directly, but it is preferable to use a configuration utility such as passwd to
make the changes. A corrupt /etc/passwd file can easily render a Linux box
unusable.
|
|
/etc/resolv.conf
|
contains a list of domain name servers used by the
local machine
|
|
/etc/X11/XF86Config
|
X
configuration file. The location in Slackware is
/etc/XF86Config.
|
|
/proc/cpuinfo
|
cpu
information
|
|
/proc/filesystems
|
prints filesystems currently in use
|
|
/proc/interrupts
|
prints interrupts currently in use
|
|
/proc/ioports
|
contains a list of the i/o addresses used by various
devices connected to the computer
|
|
/var/log/daemon.log
|
messages from service tasks like
lircd
|
|
/var/log/kern.log
|
if
something has gone wrong with a kernel module, you may find something
here.
|
|
/var/log/Xorg.0.log
|
start up log from the X server (GUI
environment), including hardware detection and modes (resolution)
selected
|
|
/etc/inittab
|
Runs
different programs and processes on start up. This is typically the program
which is responsible for, among other things, setting the default run level,
running the rc.sysinit script contained in /etc/rc.d,
setting up virtual login terminals, bringing down the system in an orderly
fashion in response to [Ctrl][Alt][Del], running the rc script in
/etc/rc.d, and running xdm for a graphical login prompt (only if the default run level is set for a graphical login). Describes how the INIT process should set up the system in various runlevels |
|
/etc/securetty
|
Contains a list of terminals on which root can login.
For security reasons, this should not include dialup
terminals.
|
|
/etc/aliases
|
File
containing aliases used by sendmail and other MTAs (mail transport
agents).
After updating this file, it is necessary to run the
new aliases utility for the changes to be passed to sendmail.
|
|
/var/spool/cron
|
User crontabs are stored
here
|
|
/etc/sysconfig/selinux
|
Policy for a system (enforcing ,permissive
,disabled)
|
Apache Tomcat
|
File
|
Description
|
|
/usr/share/tomcat5/
|
Installation directory of
Tomcat
|
|
psa-webapps
|
Installation directory for webapps in a vhost
environment
|
|
/usr/share/tomcat5/conf
|
Configuration Directory for
Tomcat
|
|
/etc/default/tomcat5
|
Contains default settings for tomcat. Most important
the used java version (jdk).
|
|
/var/log/tomcat5
|
Log files of tomcat
|
|
/etc/init.d/tomcat5
restart
|
Restart the tomcat
webserver
|
Network
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
lspci -nn | grep -i
net
|
lspci is a command on Unix-like operating systems that
prints ("lists") detailed information about all PCI buses and devices in the
system
|
|
lsusb
|
lsusb is a utility for displaying information about
USB buses in the system and the devices connected to
them
|
|
iwconfig
|
iwconfig is similar to ifconfig, but is dedicated to
wireless networking interfaces. It is used to set the parameters of the network
interface which are specific to the wireless operation (eg. frequency,
SSID)
|
|
ifconfig
|
Shows the network
connections
|
|
lsmod
|
lsmod is a command on Linux systems. It shows which
loadable kernel modules are currently loaded
|
|
python -m
SimpleHTTPServer
|
Start webserver serving current directory tree at
http://localhost:8000/
|
Some Daily Useful Commands Below:
Unix
dmidecode
-s system-product-name;lspci | grep
-i vmware
dos2unix
yum update -x kernel
df -Ph
lsb_release -a
nohup
./script.sh & (continuously run)
stat file or ls -il file for
inode
script -a /tmp/filename
ntpq -pn l ntpupdate
rpcinfo -p
ntsysv --level3
modprobe ;lsmod;modinfo
W;tty
ldd
(packages dependencies)
rpm2cpio *.rpm |cpio -ivd
rpm -Uvh --rollback '1 hour
ago'
rpm -Uvh --rollback 'March
20'
yum history rollback
46
yum history info 46
yum history undo 46
yum history repeat 46
du -h -x --max-depth=2 | egrep
"[0-9](M|G)"
du -Th --max-depth=1
/export/data/ndmwbx-vwh114-0/web/jrun4.0
Deleting files in current directory older than 7
days
find
. -type f -mtime +7 -print
| xargs rm -rf {} \;
Log Rotation
logrotate --force
/etc/logrotate.conf
Remotely Force a Reboot:
If you need to remotely hard-reset your Linux system
because of a read-only file system, try Magic
SysRq:
# echo 1 >/proc/sys/kernel/sysrq ; echo b
>/proc/sysrq-trigger
This will enable SYSRQ and power cycle the system, like
hitting the reset button. This is obviously a last resort, only when a clean
shutdown will not work.
Windows
1.wmic os get osarchitecture ; wmic
os get Name ;msinfo32
2.wmic os where primary= true call reboot ; shutdown -r
-t 10
3.systeminfo |find /I "system type"
systeminfo | findstr /C:"Total Physical
Memory"
4.mstsc /v:0.0.0.0
/f /console ;mstsc
/v:0.0.0.0 /f /admin
5. Remove
dir older than 7 days:
c:\bin\UnixUtils\find -maxdepth 1 -type d -mtime +6
-exec c:\bin\unixutils\rm -rfv {} ;
6.NTP Time
Synchronisation
- w32tm /query /configuration
- w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:ndminf-ntp001 /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
- w32tm /config /update
- net time /domain /set
- net stop w32time && net start w32time
7.Automaticallt RDP using
batchscript
cmdkey /generic:"computername or IP" /user:"username" /pass:"password" mstsc /v:"computer name or IP"
8.find out which Domain Controller my PC is talking
to
nltest
/dsgetdc:domain_name
nltest /dclist:can.edgemcolo.com