The way on how you can reset a forgotten root password on a Linux system
have not changed for many years. Resetting a root password on RHEL7
Linux system have not change much except that now we deal with

Once you hit
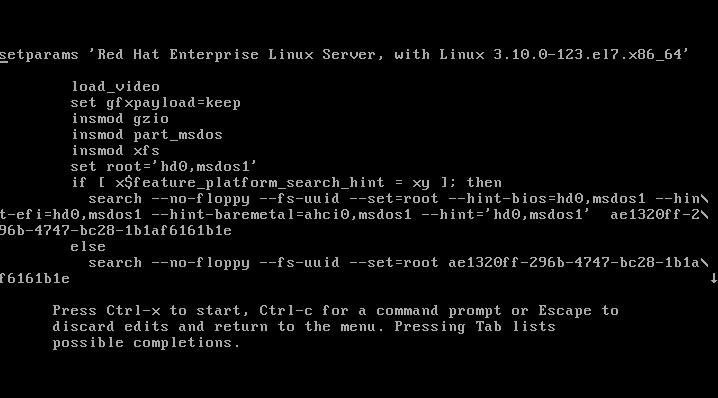
Depending
on you terminal screen size you may see more or less information. In
case you have a small terminal screen size note the little down pointing
arrow on the right edge of your screen. The arrow means that more text
is available when scrolling down. Scroll down and locate a line with

Move your cursor ( HINT: move to end of the line with CTRL+E ) on
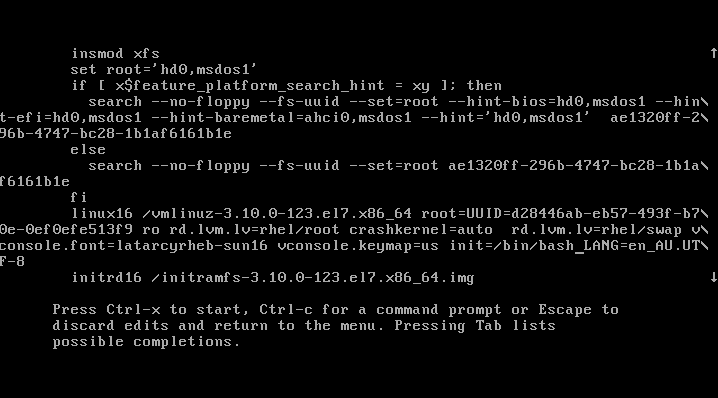
Once you edit the boot line as show above press




Normally resetting the root password is a simple task if you’re logged in already with root privileges, however if you forget the password and need to change it things become a little more difficult.
The process has changed from CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) version 6 to 7, as previously you would boot into single user mode and then change the password as root. From version 7 the equivalent modes are the rescue or emergency targets, however these require the root password before you can do anything which doesn’t help us here, so we’ll take you through the new process to change the lost root password.
This is also a task that you will need to know how to perform for the RHCSA exam.
This procedure will be completed in the console of the Linux system, so be sure that you have access to this prior to beginning. As with all system maintenance tasks, be sure you have a system backup/snapshot prior to proceeding.
After exiting the chroot and the initramfs root shell prompt the file system will be relabelled which may take a few minutes or more depending on the number of files you have. When your system has booted back up you’ll be able to use the new root password.
SElinux and the system is now using systemd instead of init.
Nevertheless, those who have already did reset root password on the
Linux system will be with the following steps familiar. Here is the
procedure of what needs to be done in order to recover a forgotten root
password on Redhat 7 Linux:- We need to edit GRUB2 boot menu and enter user single mode
- Next, we need to remount
/partition to allow read and write - Reset the actual root password
- Set entire system for SElinux relabeling after first reboot
- Reboot the system from a single mode
Edit GRUB2 boot menu
Start your system and once you see your GRUB2 boot menu usee key to edit your default boot item. Usually it is the first line: 
e key you will see a screen similar to the one below: 
rhgb quiet keywords: 
rhgb quiet keywords and replace them with init=/bin/bash as show below: 
CTRL + x to start booting your RHEL 7 system into a single mode. At the end of the system boot you will enter a single mode: 
Read&Write root partition remount
Once you enter a single your root partition is mounted as Read Onlyro. You ca confirm it with the following linux command: # mount | grep rootIn order to mount our partition with Read/Write flag we use
mount with a remount option as follows: # mount -o remount,rw /Next, confirm that the root file system is mounted Read/Write
rw: # mount | grep rootAll the above steps are show below:

Change root's password
Still in the single mode we can proceed with the actual root password recovery. To do this we usepasswd command: # passwdYou will need to enter your password twice as shown below:

SELinux relabeling
The additional step which needs to be taken on SELinux enables Linux system is to relabel SELinux context. If this step is ommited you will not be able to login with your new root password. The following linux command will ensure that the SELinux context for entire system is relabeled after reboot:# touch /.autorelabel

Reboot System
The final step when resetting your lost root password on RHEL 7 linux system is to reboot. This can be done with a following linux command:# exec /sbin/initAfter reboot you will be able to use your new root password.
Normally resetting the root password is a simple task if you’re logged in already with root privileges, however if you forget the password and need to change it things become a little more difficult.
The process has changed from CentOS/RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) version 6 to 7, as previously you would boot into single user mode and then change the password as root. From version 7 the equivalent modes are the rescue or emergency targets, however these require the root password before you can do anything which doesn’t help us here, so we’ll take you through the new process to change the lost root password.
This is also a task that you will need to know how to perform for the RHCSA exam.
This procedure will be completed in the console of the Linux system, so be sure that you have access to this prior to beginning. As with all system maintenance tasks, be sure you have a system backup/snapshot prior to proceeding.
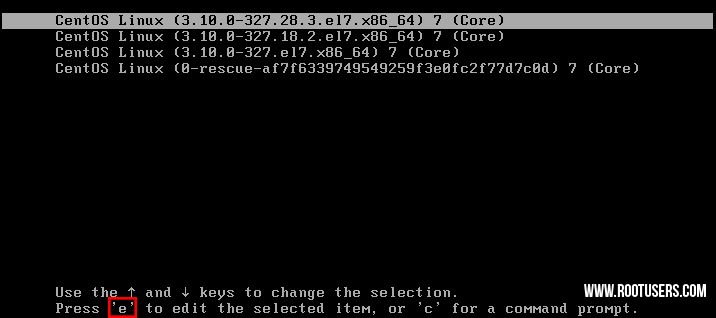
- If your Linux system is currently running, reboot
it. If it is not yet running, start it up. At the boot menu, press the
‘e’ key to edit the first boot entry.
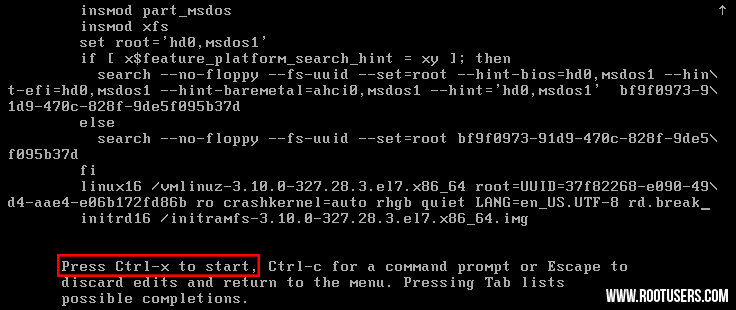
- From
the grub options, find the line that starts with “linux16” and go to
the end of it. Enter ‘rd.break’ without quotes at the end of this line,
as shown below.
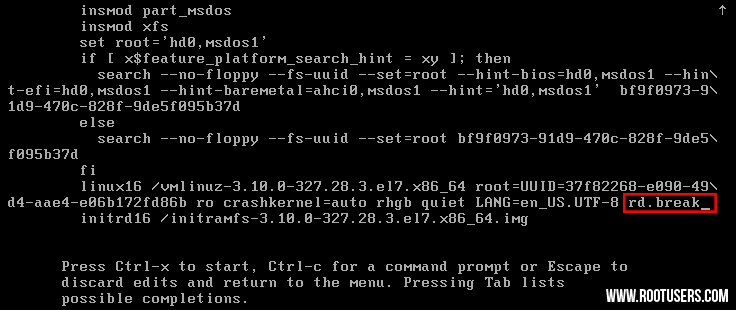
- Press “Ctrl+x” to boot with these options. This will boot to the initramfs prompt with a root shell.
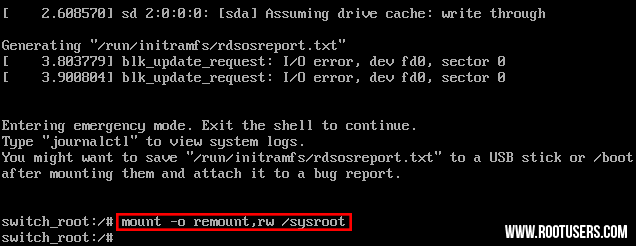
- At
this stage, the root file system is mounted in read only mode to
/sysroot and must be remounted with read/write (rw) permissions in order
for us to actually make any changes. This is done with the ‘mount -o
remount,rw /sysroot’ command.
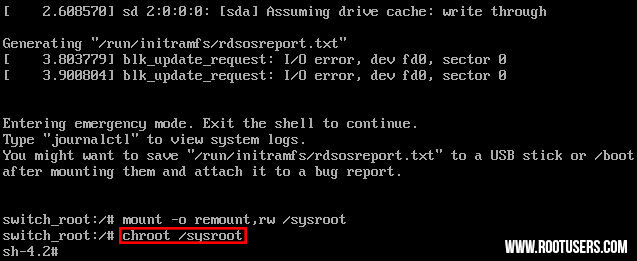
- Once
the file system has been remounted, change into a chroot jail so that
/sysroot is used as the root of the file system. This is required so
that any further commands we run will be in regards to /sysroot. This is
done by running ‘chroot /sysroot’.
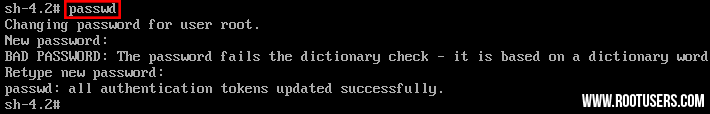
- From here the root password can be reset with the ‘passwd’ command.
- If
you’re not using SELinux, you could reboot at this point and everything
would be fine, however by default CentOS/RHEL 7 use SELinux in
enforcing mode, so we need to fix the context of the /etc/shadow file.
This is because when the ‘passwd’ command is run, it creates a new
/etc/shadow file. As SELinux is not running in this mode the file is
created with no SELinux contexts, which can cause problems when we
reboot. Create the /.autorelabel command using ‘touch’.
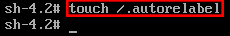
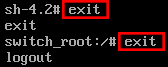
Creating this file will automatically perform a relabel of all files on next boot. Note that this may take some time depending on the amount of files you have on the file system. For a plain vanilla CentOS 7 server, it takes me about 2 minutes to complete. - Enter the ‘exit’
command twice, the first one will exit the chroot jail environment while
the second will exit the initramfs root shell and reboot the system.
Summary
As shown we can reset the root password in Linux CentOS/RHEL 7 by booting with the ‘rd.break’ option, remounting the file system with read/write privileges, creating a chroot jail, executing the passwd command and then finally fixing up SELinux contexts.After exiting the chroot and the initramfs root shell prompt the file system will be relabelled which may take a few minutes or more depending on the number of files you have. When your system has booted back up you’ll be able to use the new root password.