Puppet is an open-source configuration management tool
and server automation framework. Puppet can run on Unix-like operating systems,
as well as on the Microsoft Windows systems. It allows you to manage and perform
administrative tasks and the configuration of hundreds of systems from one
master server.
Prerequisites
- 2 or more CentOS 8 Server
- Root privileges
What we will do:
- Puppet Pre-Installation
- Install and Configure Puppet server
- Install and Configure Puppet Agent
- Verify Puppet Agent Configuration
- Create First Puppet Manifest
Step 1 - Puppet Pre-Installation
In this first step, we're going to prepare both master
and agent servers for the puppet installation. We're going to set up hosts and
FQDN of the server, setup the NTP server and add the puppet repository for
CentOS 8 server.
Setup Hostnames
Firstly, we're going to set up hosts and FQDN for both
servers. The puppet master will have a hostname 'master' with the FQDN
'master.hakase-labs.io', and the agent will have the hostname 'agent01' with the
FQDN 'agent01.hakase-labs.io'.
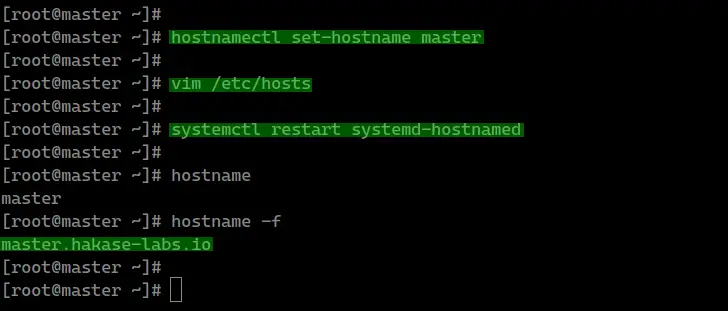
Set up the hostname using the 'hostnamectl' command
below.
hostnamectl set-hostname hostname
After that, edit the '/etc/hosts' file to configure the
FQDN server.
vim /etc/hosts
Change the IP address and the domain name with your own
and paste into it.
10.5.5.21 master.hakase-labs.io master
10.5.5.22 agent01.hakase-labs.io agent01
Save and close.
Now restart the hostnamed service to apply a new
hostname and FQDN.
systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed
And after that, check the hostname and the FQDN using
the following command.
hostname
hostname -f
And you will get a new hostname and FQDN has been
configured and applied to the system.
Setup NTP Server
For the NTP server, we're going to use "chrony" for our
servers.
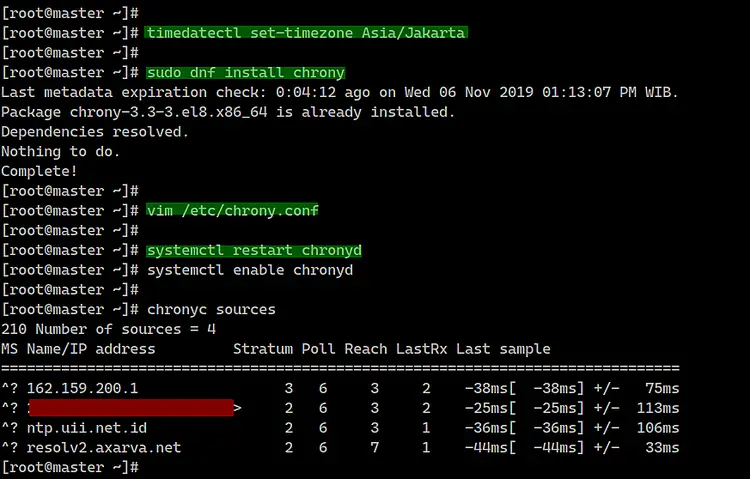
Install chrony using the dnf command below.
dnf install chrony
After that, edit the chrony configuration
'/etc/chrony.conf' using vim editor.
vim /etc/chrony.conf
Now change the pool server with the nearest pool of
your country. You can check available pool NTP using the 'https://www.pool.ntp.org/zone/COUNTRYID'.
Copy all available NTP server of your country and paste
into the 'chrony.conf' file as below.
server 0.id.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.id.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.id.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.id.pool.ntp.org iburst
Save and close.
Now start the chronyd service and add it to startup
boot time.
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
The NTP server configuration has been
completed.
Add Puppet Repository for CentOS 8
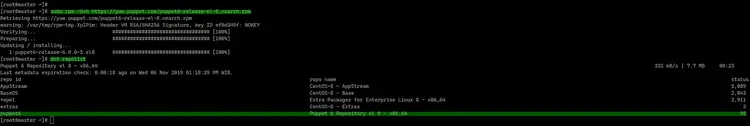
For the puppet repository CentOS 8 server, you can
install it manually using the rpm command as below.
sudo rpm -Uvh https://yum.puppet.com/puppet6-release-el-8.noarch.rpm
After that, check all available repository on the
system using the dnf command below.
dnf repolist
And you will get the puppet repository has been added
to the CentOS 8 system.
Disable SELinux
To disable the SELinux, you can edit the
'/etc/sysconfig/selinux' configuration using vim editor.
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Now change the 'SELINUX' value configuration to
"disabled".
SELINUX=disabled
Save and close, then reboot the server.
sudo reboot
Once you've logged in again, check the SELinux status
using the following command.
sestatus
And you will get the SELinux disabled
status.
Step 2 - Install and Configure Puppetserver
In this step, we're going to install and configure the
puppetserver on the master node.
Install the puppetserver using the dnf command
below.
sudo dnf install puppetserver
After that, we need to edit the 'init settings' for
puppetserver and change the memory allocation depending on the RAM that we
have.
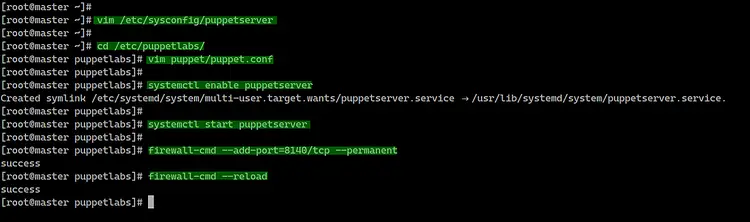
Edit the puppetserver init setting that located at the
'/etc/sysconfig/puppetserver' using vim editor.
vim /etc/sysconfig/puppetserver
Now change the 'JAVA_ARGS' configuration for memory
allocation depending on your RAM.
JAVA_ARGS="-Xms1g -Xmx1g ...."
Save and close.
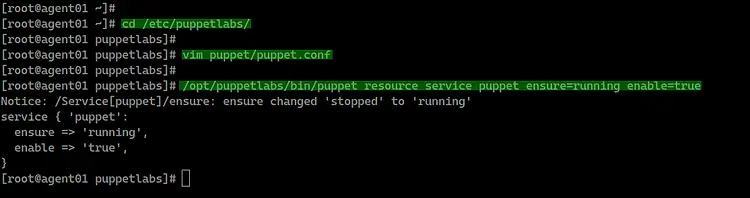
Next, go to the '/etc/puppetlabs' directory and edit
the puppet configuration file 'puppet.conf'.
cd /etc/puppetlabs/
vim puppet/puppet.conf
Under the master configuration, define the DNS
alternative names with the FQDN of the master server.
[master]
....
dns_alt_names=master.hakase-labs.io,puppet
....
After that, define the puppet main server configuration
as below.
[main]
certname = master.hakase-labs.io
server = master.hakase-labs.io
environment = production
runinterval = 1h
Save and close.
Now add the puppetserver service to the startup boot
time and start the service.
systemctl enable puppetserver
systemctl start puppetserver
The puppetserver is up and running on CentOS 8 server
with the default TCP port '8140'.
Add the puppetserver port '8140' to the firewalld using
the following command.
firewall-cmd --add-port=8140/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
And as a result, the puppet master installation and
configuration has been completed successfully.
Step 3 - Install and Configure Puppet Agent
After installing the Puppet master server
'master.hakase-labs.io', we're going to install a puppet agent on the 'agent01'
server.
Log in to the 'agent01' server and install the
puppet-agent package using the dnf command below.
sudo dnf install puppet-agent
After that, go to the '/etc/puppetlabs' directory and
edit the configuration file 'puppet.conf' using vim editor.
cd /etc/puppetlabs/
vim puppet/puppet.conf
Change the 'certname' and 'server' configuration with
your own and paste to the configuration.
[main]
certname = agent01.hakase-labs.io
server = master.hakase-labs.io
environment = production
runinterval = 1h
Save and close.
Next, start puppet service and register the Puppet
agent to the master server using the following command.
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet resource service puppet ensure=running enable=true
And you will get the result as below.
The puppet agent is now up and running, it's attempting
to register to the Puppet master server.
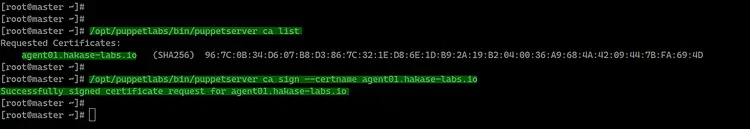
Now back to the Puppet master server and check of
pending certificate requests.
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca list
And you will get the 'agent01.hakase-labs.io'
certificate on the list.
Now sign the 'agent01' certificate using the command
below.
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca sign --certname agent01.hakase-labs.io
And the puppet agent is now has been registered to the
master server.
Step 4 - Verify Puppet Agent Configuration
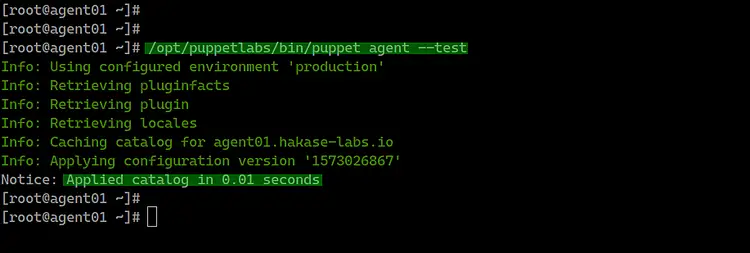
Now verify the Puppet agent configuration and test the
connection between the puppet agent and master using the following
command.
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
And you will get the result as below.
As a result, the Puppet agent pulled the configuration
from the puppet master and applied it to the server without any
error.
Step 5 - Create First Manifest
At this stage, the installation and configuration of
Puppet for master and agent have been completed.
And for this step, we're going to test our setup by
creating the first puppet manifest for installing the httpd package.
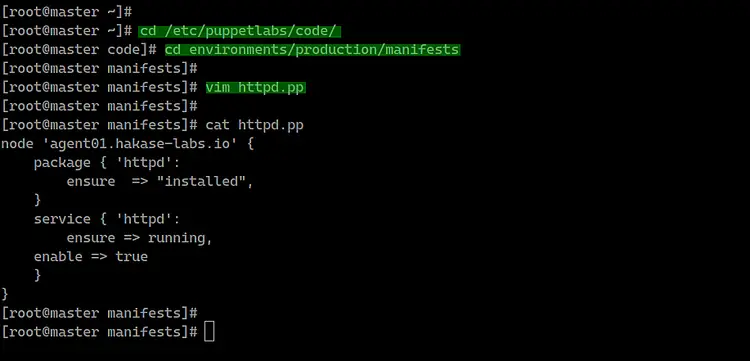
Go to the
'/etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/manifests' directory and create
the first puppet manifest file 'httpd.pp'.
cd /etc/puppetlabs/code/
cd environments/production/manifests
vim httpd.pp
Paste the following configuration.
node 'agent01.hakase-labs.io' {
package { 'httpd':
ensure => "installed",
}
service { 'httpd':
ensure => running,
enable => true
}
}
Save and close.
Now go to the Puppet agent node 'agento01' and run the
following command.
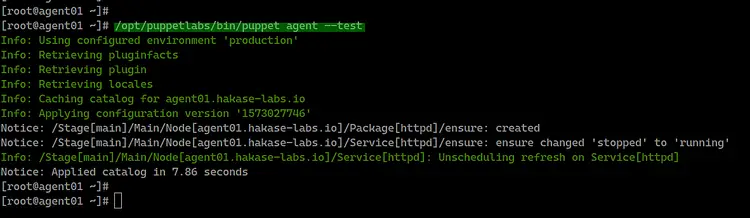
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
And you will be shown the result as below.
The Puppet agent pulled a new configuration from the
Puppet master for installing the httpd package and start the httpd
service.
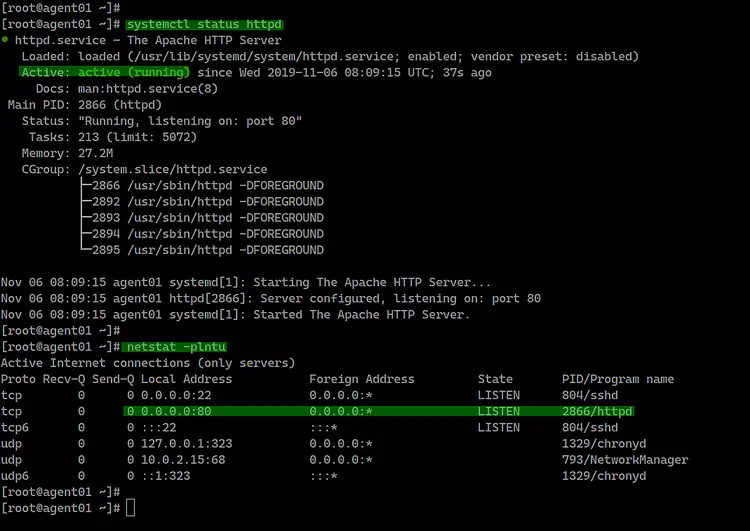
On the 'agent01' node, check the httpd service status
and check the HTTP port '80'
systemctl status httpd
netstat -plntu
And you will get the httpd service is up and running on
the 'agent01' server with the default HTTP port '80'. The httpd package has been
installed through the puppet manifest that we've created at the top.